How Far Can My Eyes See?
Have you ever looked up at the stars on a clear night and wondered just how far the human eye can see? It’s a fascinating question with an even more amazing answer: healthy eyes can detect objects millions, even billions, of miles away!
The naked eye has the capability of seeing a distant object light-years away under the right conditions. Your eye’s line of sight, the brightness of light from the object, and your eye health determine how far you can see.
Key Points
- The distance from which you can see an object depends on how bright it is and if nothing is blocking your view.
- Visual acuity is a measure of how clear your vision is.
- The health of your eyes, any vision prescription you might need, and various eye imperfections and parts influence your ability to see.
How Far Can The Human Eye See?
The answer depends on which way you’re looking. Due to the curvature of the earth, the farthest object the human eye can see on earth is about 3 miles. How far could the human eye see if the earth was flat? If the earth was flat or you were standing on top of a mountain, you could see bright lights in the distance hundreds of miles away.1
On the other hand, if you’re viewing the sky on a clear, dark night that distance is measured in millions and billions of miles. Exactly how far can the human eye see? Several factors affect the distance you can see so let’s take a closer look.
Seeing Far vs. Seeing Clearly
Your eyes are incredibly sensitive to light, which is why you can see stars and galaxies even though they’re unimaginably far away. The Andromeda Galaxy, our nearest galactic neighbor, is a perfect example. Located about 2.5 million light-years from Earth, it’s visible to the naked eye as a faint, smudgy patch in the night sky—no telescope required! According to researchers, the Andromeda Galaxy contains hundreds of billions of stars, many of which contribute to the faint glow we see on clear, dark nights.2
But there’s a difference between detecting light and seeing something clearly. The farther away an object is, the harder it is for your eyes to make out details. That’s why you can’t read a road sign from miles away, even if you can see the sign itself.
Exclusive offers
Receive exclusive offers about eye health and wellness, courses, and more!

Visual Acuity and The Human Eye
When your vision is checked by an eye doctor (optometrist or ophthalmologist) 20/20 is considered normal vision. Visual acuity is a measurement of your ability to see a distance object or a near object and taken using a Snellen chart. The measurement of vision is based on what a “normal” person can see at a distance of 20 feet. For example, 20/20 vision means the patient can see the same as what a normal person sees at 20 feet. Visual acuity is the smallest retinal image appreciated by the eye.3
Eye Health
Eye health can affect your visual acuity. Any eye condition can limit your vision. Conditions of the cornea like keratoconus cause aberrations in vision and even distort the patient’s view. Similarly, cataracts can cause obstructions in your central line of sight and distort colors. Diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration, and glaucoma are other eye conditions that can make it difficult to see well.4
Your eye’s clarity and sharpness are measured during an eye exam. Your vision can be affected by uncorrected refractive error and various conditions that affect eye health.

All Rounder
Eyelid Hygiene Plan 3
Perfect for eye dryness, burning, itching, grittiness, crusting/flaking of eyelashes and inflamed/swollen eyelids. Free shipping 📦.
Try today - $60
Refractive Error
If you can’t view a distant object you are considered myopic (near-sighted). Individuals with myopia have eyes with a slightly longer length than normal. However, if it is difficult to see near objects, you are hyperopic (far-sighted) with shorter eyes than normal.5
Lastly, astigmatism is one of the most common refractive errors. It occurs when parallel rays of light entering the eye are brought to focus at two distinct focal lines perpendicular to each other, rather than to a single focal point resulting in halos and glare.5
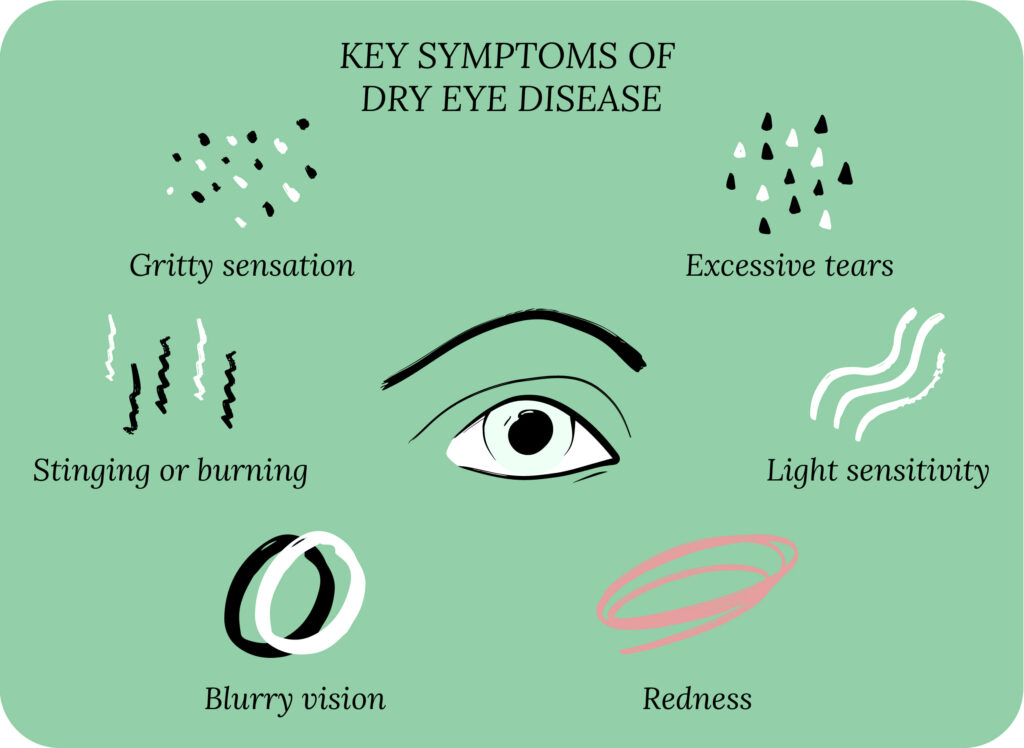
The Human Eye: How It Works
The cornea, iris, and lens make up the front of your eye. The retina and optic nerve are located in the back of the eye.
Front of the Eyeball
The cornea is the clear dome over the surface of the eye. Its purpose is to protect your eye and refract rays of light. The iris allows the appropriate amount of light to enter the retina. The iris is like the shutter of a camera. It allows enough light to enter your eye to activate the retina. The iris dilates in the dark and constricts in the light, allowing more bright light through the pupil under scotopic (dark) conditions than under photopic conditions (light).
For this reason, when driving, it may be more difficult to see a distant object on a dark night compared to a clear day. Made of tissue, the crystalline lens can change its shape to adjust the power of the eye and to focus the image on the retina called accommodation.6
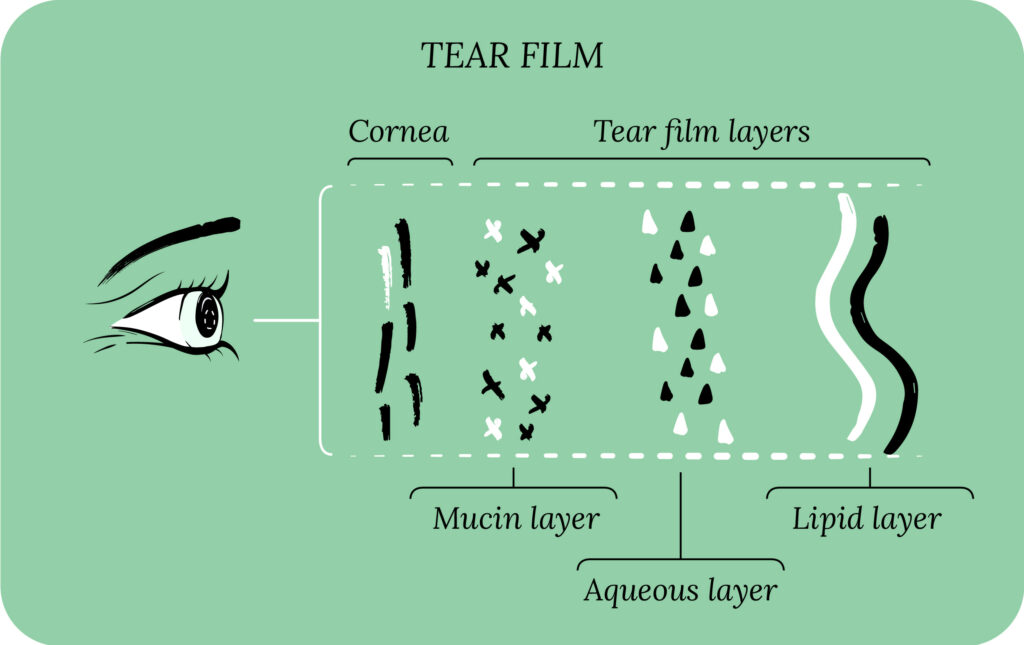
Back of the Eyeball
The retina is a layer of photoreceptors and glial cells that captures incoming photons and transmits them along neuronal pathways as both electrical and chemical signals to the brain in order to see a picture.
It is composed of two different types of cells: rod cells and cone cells. The activation of rod cells and cone cells, also called photoreceptors, initiates our vision. One type of rod cell exists for dim light vision and three types of cone cells enable one to see colors. Finally, the signals from the eyeball are sent to the brain through the optic nerve.
How Far Can Human Eye See FAQ
The ability to see a person from a distance varies based on factors like lighting and visibility conditions. Generally, human eyes can discern people at different distances, with clear vision diminishing as the distance increases.
Clear vision is subjective and varies among individuals. However, in standard eye exams, the benchmark for clear vision is often considered to be 20/20. This means that a person with normal vision should be able to see clearly at a distance of 20 feet.
Perfect vision is commonly defined as 20/20 vision. In the context of an eye chart, it means that you can see at 20 feet what a person with normal vision can also see at 20 feet. However, perfect vision doesn’t necessarily mean flawless eyesight; it implies having visual acuity within the average range.
Rest
Warm Compresses
Perfect for eye dryness, fatigue, tearing, and puffiness of the eyelids. Free shipping 📦.
Try today - $30
Putting It All Together
The capability of human vision remains unknown though a bright object and an unobstructed view are important to see a distance object like the Andromeda galaxy. Additionally, the visual acuity of the human eye is affected by eye health and refractive error. Types of ocular pathology like age-related macular degeneration of astigmatism can have an affect on how the eye sees. Furthermore, visiting an eye doctor to have your vision checked, and your glasses prescription updated is vital to optimizing the capabilities of the eye.
What’s Next
Learn to love your eyes! Read more eye health and wellness tips on our blog.




